Hi all. This is probably the funniest thing I have done in my professional life – trying to make Software Engineering exciting ? Why you make ask… or how you may ask… well, as usual, I’ve got a short answer and a long answer. The short answer is to ensure that I myself am exciting about this piece of art (yes, not science, day by day I am discovering there software engineering is more art than science, hence making the word engineering more of an oxymoron!) and rediscover the very reason I got into this it – my passion!
The long answer is pretty long… so long that its gonna span few articles – which will be the articles I’lll be writing in the next few weeks or months (I hope). I hope to cover various topics in Software Engineering… but not from the technical point of views… I believe that there are tons and tons of technical papers out there to last a life time of humans (before they kill themselves and this planet!).
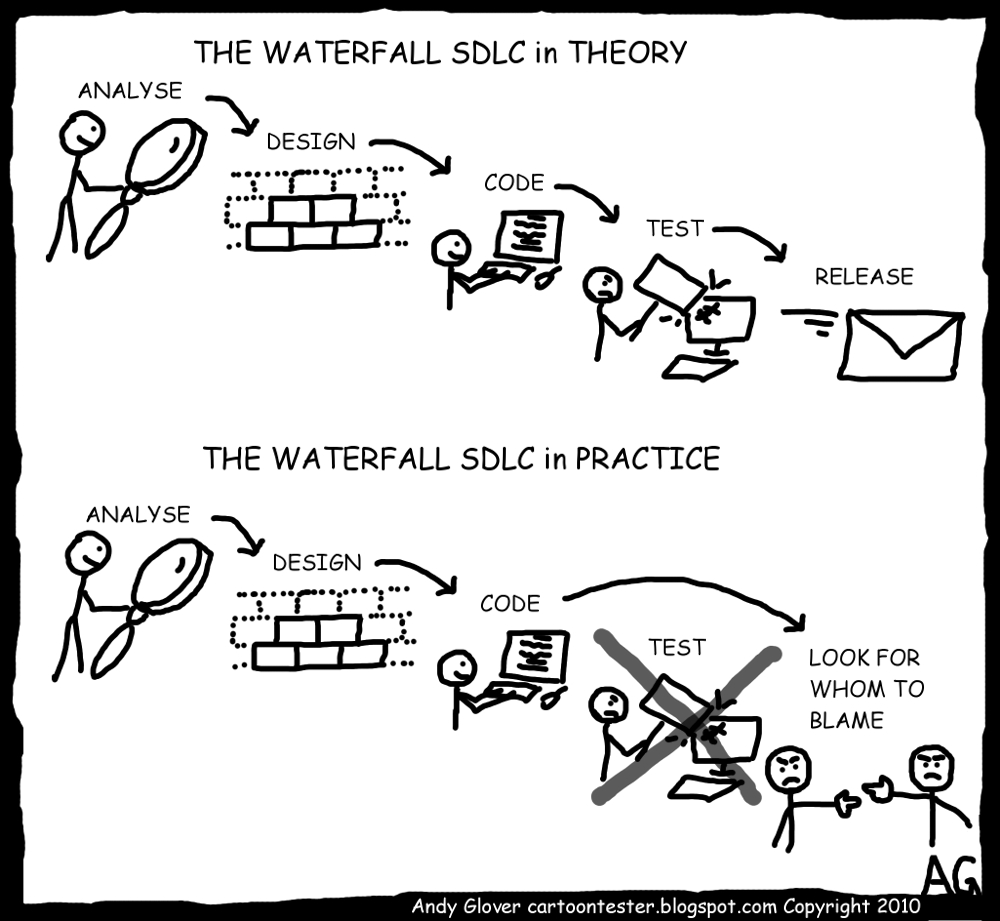
The objective of these articles are to discuss the day to say issues, risks, progress, and anything got to do with our dear SDLCs – yes, Software Development Life Cycle. The fact that we are still using waterfall model lifecycle just blows my mind! Did you know that waterfall model was first introduced in 1956 by a guy called Herbert? (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waterfall_model). I am not saying that waterfall model cant be used, but the fact that many projects still use the 57 year old waterfall or modified waterfall model to develop “cutting edge” 21st centry solution is really mind blowing.
Does the Famous SDLC Waterfall Model work?
Nevertheless waterfall makes Software Engineering more comprehensible to the non-IT people out there.
Or is it otherwise? Well, before you can commet, it is best to understand what is Waterfall model?
I am quoting my friend – Shah Newaz Alam’s excellent article on the pros and cons of the fall (waterfall):
The Waterfall Model
The most important aspect of the waterfall model is that unless a particular stage is complete, the next stage cannot be started off with. Here, in this article, we will try to understand a simple waterfall model, broken into six stages. Let us try to understand each of these stages one by one.
Stage 1: Requirement Phase
Whether you design a small program to add two numbers or you are into developing a software system for the automation of an entire airline company, this is the first stage which can never be overridden. Unless you know what you are going to design, you cannot approach the problem. Here, the specifications of the output or the final product is studied and marked.
Stage 2: Specification Phase
With all the requirements and constraints in hand, a final view of how the product should exactly be, is decided. The exact way in which the software should function is mentioned in this stage.
Stage 3: Design Phase
Here the actual work begins. Every type of resource which will be required for the smooth designing of the software, is mentioned here in this phase. What type of database will be required, what type of data should be supported, etc. are some of the important aspects that are decided in this phase. The algorithm of the process in which the software needs to be designed, is made in this phase. This algorithm forms the backbone for the actual coding process, that takes place in the next phase.
Stage 4: Implementation and Testing Phase
Now starts the coding. Here, the software is coded as per the algorithm. Hence it becomes very important that the algorithm should be properly designed. The software designed, needs to go through constant software testing and error correction processes to find out if there are any flaw or errors.
Stage 5: Integration and Testing Phase
Here the various codes designed by different programmers are integrated and is tested if the software works as per the specifications provided. The setup of the final software which needs to be installed at the clients system, is also designed and tested, so that the client does not face any problem during the installation of the software. The product is then handed over to the client.
Stage 6: Maintenance Phase
The cycle of software development does not end with handing the software to the client. Software designers may have to constantly provide support to the client to resolve any issues which may arise. During the maintenance phase, support and debugging is provided for all such problems.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
The waterfall model is the oldest and most widely used model in the field of software development. There are certain advantages of this model, which makes it, one of the most widely used models as yet. Some of them are:
- Being a linear model, it is very simple to implement.
- The amount of resources required to implement this model are minimal.
- Documentation is produced at every stage of the software’s development. This makes understanding the product designing procedure, simpler.
- After every major stage of software coding, testing is done to check the correct running of the code.
Disadvantages
- The question that must be bothering you now is that with so many advantages at hand, what could be the possible disadvantages of the waterfall model? Here are a few:
- Ironically, the biggest disadvantage is one of its greatest advantages. You cannot go back a step; if the design phase has gone wrong, things can get very complicated in the implementation phase.
- Often, the client is not very clear of what he exactly wants from the software. Any changes that he mentions in between, may cause a lot of confusion.
- Small changes or errors that arise in the completed software may cause a lot of problems.
- Until the final stage of the development cycle is complete, a working model of the software does not lie in the hands of the client. Thus, he is hardly in a position to inform the developers, if what has been designed is exactly what he had asked for.
- So this, in short, was all about waterfall model advantages and disadvantages. In spite of the cons, the many pros of this model ensure that it remains one of the most popular models used in the field of software development.